Topics and Sub Topics in Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation:
- Gravitation
- Gravitation
- Free Fall
- Mass
- Weight
- Thrust and Pressure
- Archimedes’ Principle
- Relative Density
These solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 10 Gravitation.
In – Text Questions Solved
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 141
Questin 1. Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
Answer: The force exerted by a thin and strong string is distributed to very less area and hence the force applied due to the bag is more, the pressure exerted on the body by thin straps will be more and hence will be more painful.
As pressure is inversely proportional to area, if the area is reduced pressure

Questin 2. What do you mean by buoyancy?
Answer: The upward force exerted by any fluid (liquid, gas) on an object is known as upthrust or buoyancy.
Questin 3. Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water?
Answer: The density of the objects and water decides the floating or sinking of the object in water.
The density of water is 1 gm/cm3.
- If the density of an object is less than the density of water then the object will float.
- If the density of an object is more than the density of water then the object will sink.
- Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 142
Questin 1. You find your mass to be 42 kg on a weighing machine. Is your mass more or less than 42 kg?
Answer: The weighing machine actually measures the weight of the body as the acceleration due to gravity ‘g’ is acting on the body. Hence the mass reading of 42 kg given by a weighing machine is same as the actual mass of the body. As mass is the quantity of inertia, it remains the same. - Questin 2. You have a bag of cotton and an iron bar, each indicating a mass of 100 kg when measured on a weighing machine. In reality, one is heavier than other. Can you say which one is heavier and why?
Answer: The heaviness of the bag can be given by densityMass of both cotton bag and iron bag is same. But the volume of cotton bag is more than the iron bag.
Hence density is inversely proportional to volume. The bag of iron will be heavier. - Questions From NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science
- Question 19. In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
Answer: The buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid acts upwards, i.e. opposite to the direction of the force exerted by the object. - Question 20. Why does a block of plastic released under water come up to the surface of water?
Answer. The floating or sinking of a body in the water is decided by the density of both the body and water’s buoyant force acting on the body by the liquid.
The density of plastic is less than the water and the buoyant force exerted by water on the plastiq block is greater than the force exerted by plastic on the water. - Questin 21. The volume of 50 g of a substance is 20 cm3. If the density of water is 1 gem 3, will the substance float or sink?
Answer.
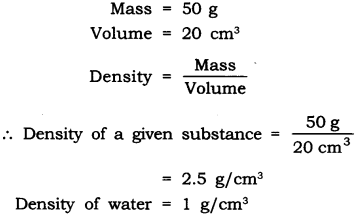
As the density of a given substance is more than the density of water. The substance will sink in water.
Question 22. The volume of a 500 g sealed packet is 350 cm3. Will the packet float or sink in water if the density of water is lg cmr3? What will be the mass of the water displaced by this packet?
Answer:






